Giza in Egypt | The history icon of geotechnical engineering | iStock Paid Download
Unlock the hidden potential of geotechnical service with advanced soil testing techniques that reveal the secrets of soil, rock, and groundwater. As geotechnical engineers design foundations, retaining walls, slopes, and embankments, they play a vital role in creating a better world. Discover the rich history of geotechnical engineering, from its ancient origins to its modern-day innovations, and learn about the incredible impact this field has on our daily lives.
UNVEILING THE EARLY STAGES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
Geotechnical services can be traced back to ancient times when humans built earthworks such as earthen embankments and terraced fields. The ancient Egyptians, for example, built the Great Pyramids of Giza on a limestone bedrock plateau, and they used an earthen ramp system to transport the massive stones used to build the pyramids. The ancient Greeks also contributed significantly to geotechnical engineering, such as the construction of roads and aqueducts that required extensive earthworks.
THE IMPACT OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
There was a renewed interest in the study of the natural world during the Renaissance, and many advances were made in the field of geotechnical services. Leonardo da Vinci, for example, was a skilled engineer and artist who drew numerous sketches of earth-moving machinery and proposed new foundation-building methods. Andrea Palladio, an Italian architect, and engineer, wrote extensively on foundations and soil mechanics in the 16th century, and he is credited with developing the concept of soil-bearing capacity.
THE SOIL TESTING INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
The Industrial Revolution resulted in a significant increase in the demand for geotechnical engineering expertise. Engineers faced new challenges as cities grew and industrialization spread, such as the construction of large-scale infrastructure projects like canals, railways, and bridges. The construction of the Thames Tunnel in London was one of the most notable examples of geotechnical services at the time. The tunnel, which opened in 1843, was the first to be built beneath a navigable river and required extensive excavation and ground support measures.
EXPLORING THE WONDERS OF MODERN GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
The rise of smart technological engineering, however, is perhaps the most exciting development in modern geotechnical engineering. Smart geotechnical engineering combines sensors, data analysis, and automation to create intelligent systems capable of monitoring and responding to environmental changes. Sensors installed in a bridge, for example, can detect changes in temperature, vibration, and stress, allowing engineers to anticipate and prevent potential problems before they occur.
Geotechnical engineering has evolved and expanded over the last century, utilizing cutting-edge technologies and materials to push the boundaries of what is possible.
The introduction of the finite element method was one of the most significant developments in geotechnical engineering. This numerical technique, which was invented in the 1950s, has transformed the way engineers solve complex problems. The finite element method allows engineers to analyze and design structures and systems with unprecedented accuracy and efficiency by breaking a problem down into smaller, more manageable parts.
But that’s not all: the introduction of digital technologies has altered the way geotechnical engineers work. Engineers can simulate and test different scenarios using powerful computers and advanced software to find the best design for any given project. Not only does this save time and money, but it also allows for greater precision and accuracy in the design process.
The applications of smart geotechnical services are truly endless. The future of geotechnical services is bright and full of potential, from self-healing materials that can repair themselves to autonomous robots that can inspect and maintain structures.
Over the last century, geotechnical engineering has come a long way, with the introduction of the finite element method and digital technologies revolutionizing the way engineers solve complex problems. Furthermore, the rise of smart geotechnical engineering has created new opportunities for monitoring and responding to environmental changes. Geotechnical engineers are pushing the boundaries of what is possible with these tools, creating structures and systems that are more efficient, precise, and resilient than ever before. It is important to note, however, that with these advances come new challenges, such as ensuring the safety and reliability of these new technologies. As with any field, it’s critical to strike a balance between the benefits of innovation and the need for responsible, ethical behavior.
Throughout history, there have been numerous notable geotechnical engineering projects, some of which include:
THE TRIUMPH OF THE PANAMA CANAL
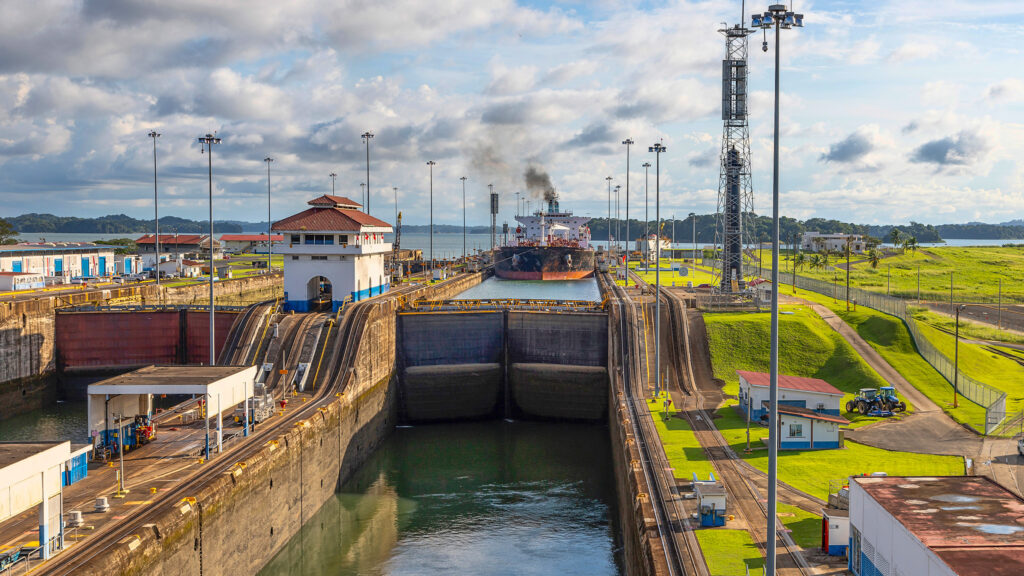

The Panama Canal was a massive undertaking that required extensive excavation and ground stabilization measures in the early twentieth century. Engineers had to deal with difficult soil conditions such as soft clays and volcanic rock, as well as the tropical climate and the presence of diseases such as yellow fever.
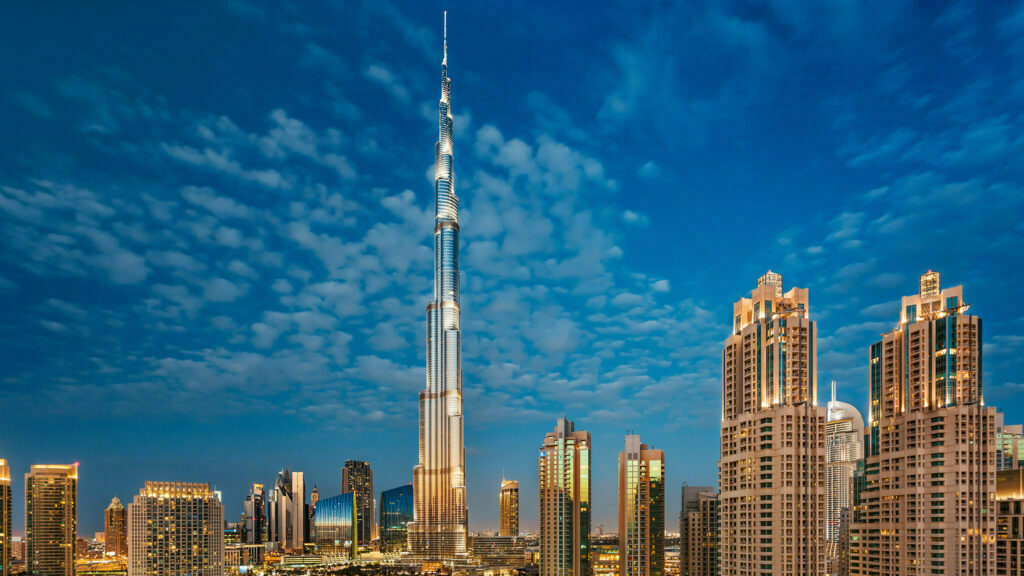
SOARING OF BURJ KHALIFA
The Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the world’s tallest building, required extensive geotechnical analysis and design. The foundation of the building is a massive concrete raft supported by piles that extend over 50 meters into the ground. The effects of the building’s weight on the underlying soil, as well as the possibility of settlement and other issues, had to be considered in the design.

MARVEL OF MILLAU VIADUCT
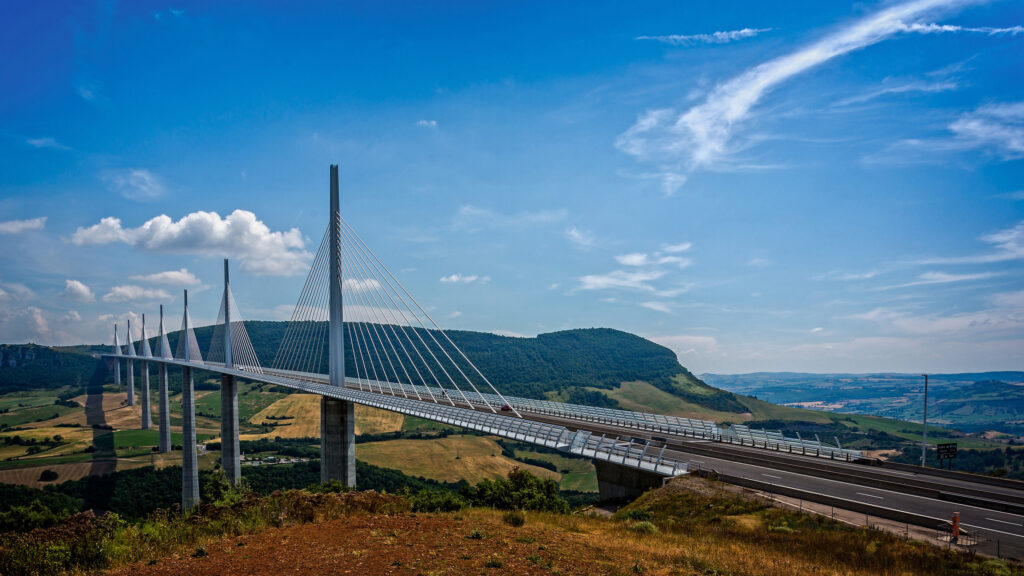

In southern France, the Millau Viaduct is a cable-stayed bridge that spans the Tarn River valley. To ensure stability and prevent collapse, the bridge’s foundations required extensive geotechnical analysis and design, including the use of deep foundation elements and soil reinforcement measures.
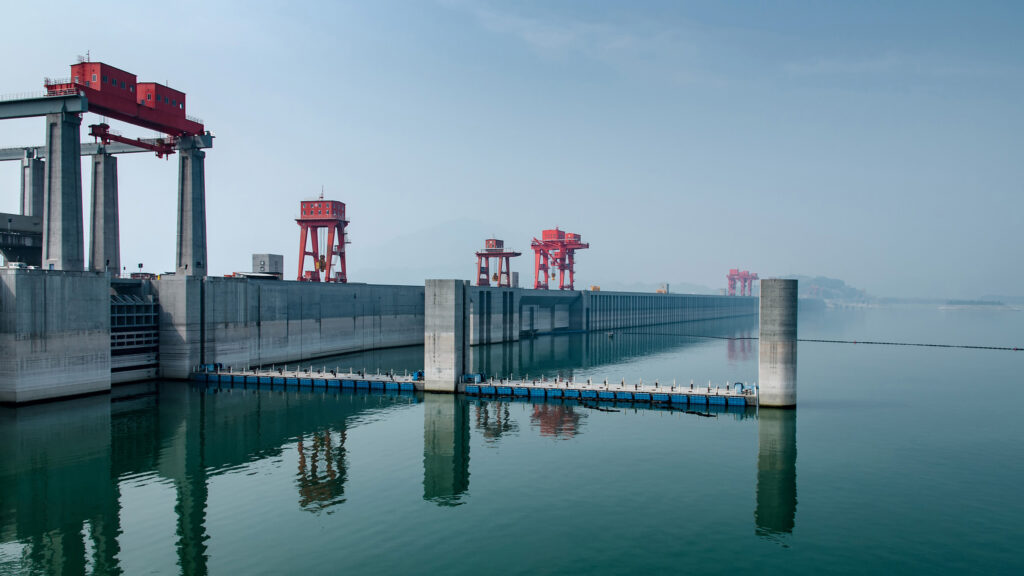
POWERING OF THE THREE GORGES DAM
China’s Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River is one of the world’s largest hydroelectric power stations. The dam’s construction necessitated extensive geotechnical analysis and design, as well as measures to stabilize surrounding hillsides and prevent landslides. The foundation of the dam is a massive concrete slab that was poured in sections over several years.

CONQUERING THE OCEAN OF DUBAI PALM ISLANDS
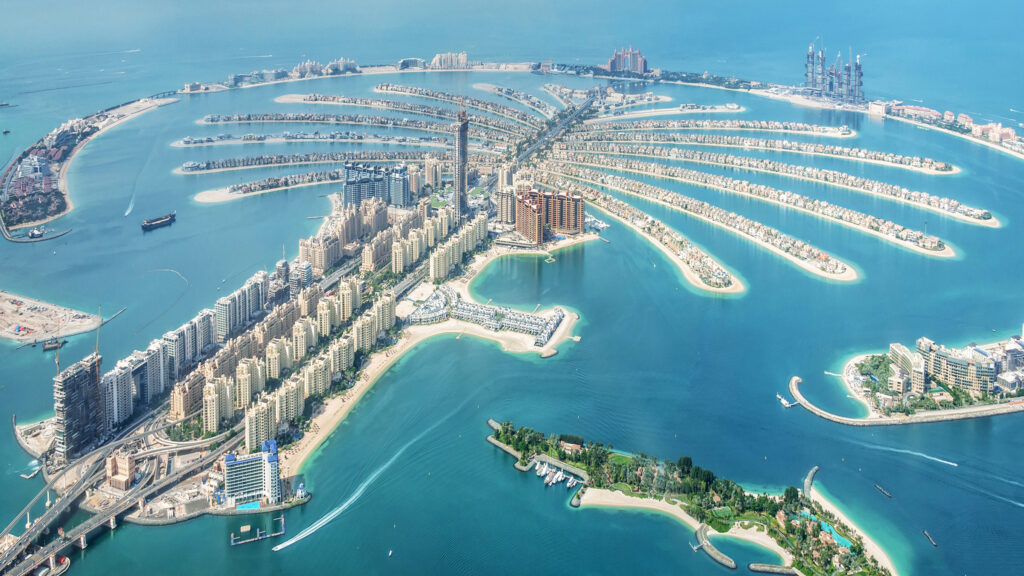

The Dubai Palm Islands are a group of man-made islands built off the coast of Dubai in the early 2000s. The islands’ construction necessitated extensive geotechnical analysis and design, as well as measures to stabilize the underlying seabed and prevent erosion. A network of massive concrete piles extending up to 45 meters into the seabed supports the islands.
CONCLUSION
Geotechnical engineering has a fascinating and long history that dates back thousands of years. People have been designing and building structures on earth for centuries, from the ancient Egyptians to modern-day engineers. The need to solve increasingly complex engineering challenges has driven the evolution and expansion of the field of geotechnical engineering. Geotechnical engineers today design and analyze earth structures ranging from skyscrapers and bridges to dams and artificial islands using a variety of advanced technologies and techniques. We can gain a better appreciation for the many remarkable feats of engineering that have been accomplished throughout history, as well as the ongoing challenges and opportunities that lie ahead, by studying the history of geotechnical engineering.
